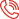Why Epoxy Injection Matters for Your Foundation
Epoxy injection is a proven method for repairing structural cracks in concrete by injecting high-strength resin into damaged areas to restore original strength and prevent moisture intrusion. Here’s what you need to know:
Key Facts About Epoxy Injection:
- Purpose: Repairs structural cracks in concrete foundations, walls, beams, and columns
- Crack Range: Effective for cracks from 0.002 inches (0.05 mm) to 1/4 inch wide
- Bond Strength: The bond strength of epoxy to clean concrete exceeds the tensile strength of concrete itself
- Best For: Dormant (non-moving) structural cracks in dry to slightly damp conditions
- Not Suitable For: Active water leaks, moving cracks, or cracks caused by ongoing corrosion
- Typical Cost: Professional crack repair ranges from $300-$800 per crack; full basement waterproofing averages $4K-$8K
Cracked concrete isn’t just an eyesore. It’s a structural concern that can compromise your home’s foundation and allow water, pests, and even radon gas into your basement. Left untreated, cracks can widen over time, leading to costly repairs that may reach $11,000 or more.
The good news? Epoxy injection can restore cracked concrete to its original strength when applied correctly. This repair method uses low-viscosity epoxy resin injected under pressure to completely fill and bond crack surfaces together. The result is a repair that’s often stronger than the surrounding concrete.
But epoxy injection isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It works best for structural repairs on dormant cracks where the primary goal is restoring strength and preventing moisture penetration. If you’re dealing with active leaks or cracks that continue to move, other methods like polyurethane injection or crystalline waterproofing may be more appropriate.
Understanding when and how to use epoxy injection can save you thousands in unnecessary repairs and prevent temporary fixes that fail within months. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about the process, from identifying suitable cracks to verifying a successful repair.
I’m Darin Garvey, and over my 30+ years in basement waterproofing, I’ve seen countless foundation repairs—both successful and failed. Through extensive work with epoxy injection for structural crack repair, I’ve learned what separates lasting solutions from temporary patches. Let me share that knowledge with you.
Epoxy injection terms to learn:
Understanding Epoxy Injection for Concrete Repair
When we talk about concrete repair, epoxy injection is a highly effective, polymer delivery method that we use through a specialized pumping system. It works by injecting a low-viscosity epoxy resin directly into cracks in concrete structures. This process effectively seals all accessible sides of a crack and bonds them together, restoring the concrete’s original strength and preventing further issues.
The magic of epoxy injection lies in its ability to create a strong, impermeable bond. The epoxy resin, once injected, flows into the crack, fills it completely, and then cures to form a solid mass. This cured epoxy often possesses tensile and compressive strengths that are higher than the concrete itself, ensuring a permanent and durable load transfer. This means the repaired area becomes as strong, if not stronger, than the surrounding concrete, effectively reversing the structural damage caused by the crack. Beyond structural restoration, epoxy injection also provides excellent resistance to moisture penetration, helping to keep your basement dry and healthy.
For more detailed information on various concrete repair methods, we recommend checking out resources like More info about concrete crack repair.
What Types of Cracks Are Suitable?
Not all cracks are created equal, and neither are their repair solutions. Epoxy injection is specifically designed for structural cracks that are dormant, meaning they are not actively moving or expanding.
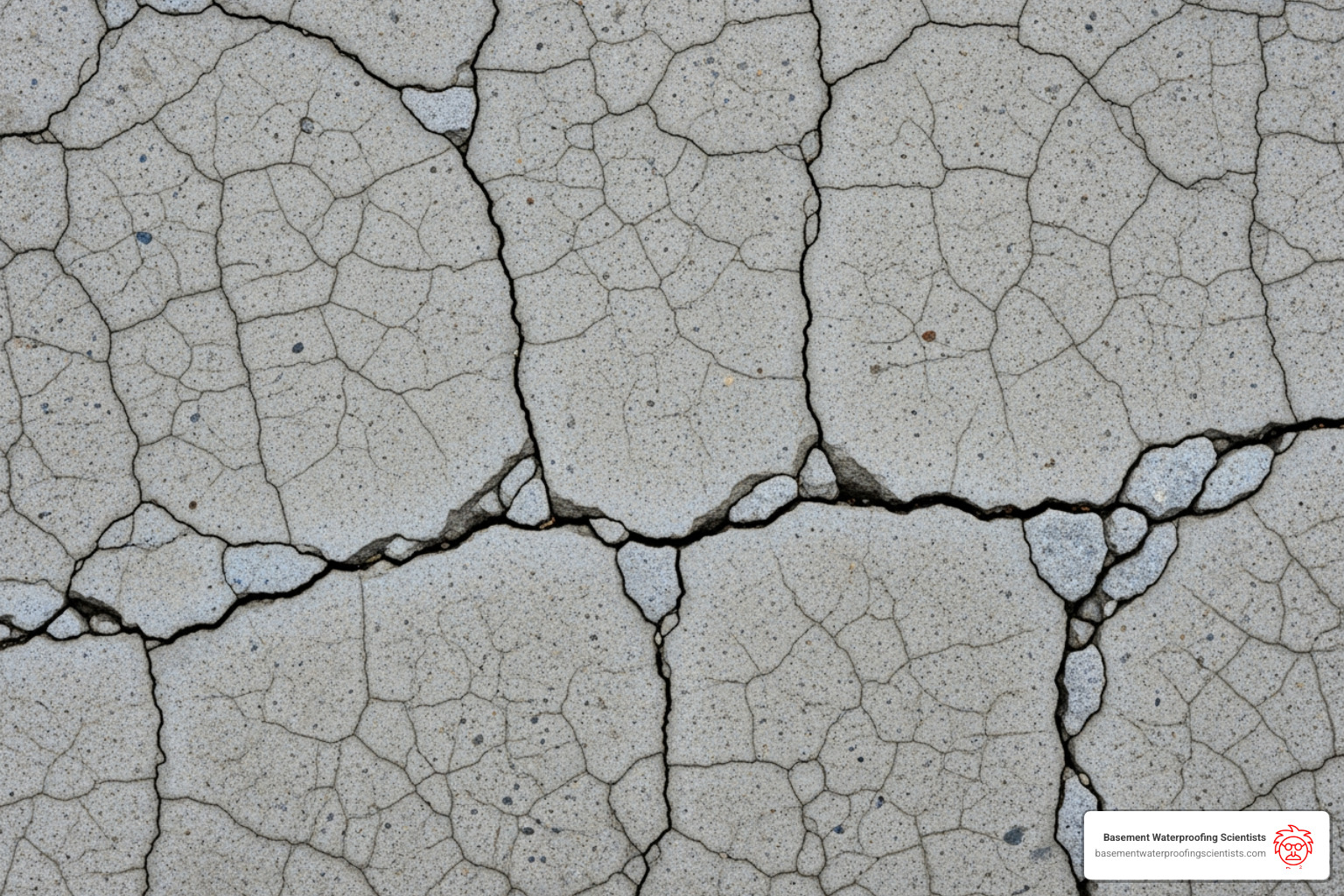

We typically use epoxy injection for cracks ranging from 0.002 inches (0.05 mm) up to 1/4 inch wide. This covers a significant range, from hairline cracks to more substantial fissures. These cracks are commonly found in:
- Foundation walls: Restoring the integrity of your home’s base.
- Beams and columns: Essential for supporting overhead loads.
- Slabs: Ensuring the stability of floors and other horizontal surfaces.
For very fine cracks, a low-viscosity epoxy (500 cps or less) is crucial for deep penetration. Our team carefully inspects each crack to determine its nature and width, ensuring that epoxy injection is the appropriate solution. For smaller, non-structural cracks, homeowners might find useful tips in our guide on Small Foundation Cracks Homeowner Tips.
Common Applications and Industries
The versatility and strength of epoxy injection make it a preferred repair method across various applications and industries, especially where structural integrity is paramount. In our service areas across Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware, we frequently apply epoxy injection in:
- Residential foundations and basements: This is our bread and butter, ensuring the longevity and safety of your home, whether in Philadelphia, Pottstown, or Norristown.
- Parking garages: Repairing cracks that can lead to water infiltration and rebar corrosion.
- Commercial buildings and industrial facilities: Addressing structural damage to maintain operational safety and compliance.
- Bridges and other infrastructure: While not our primary focus, the principles of restoring strength to concrete apply universally.
Essentially, if a concrete structure has suffered damage from “one-time” events like an overload, vehicle impact, or even minor settlement that has caused a structural crack, epoxy injection can restore its integrity. It’s a key part of our strategy for Understanding Structural Basement Repair: What You Need to Know.
The Step-by-Step Epoxy Injection Process
The success of an epoxy injection repair hinges on meticulous preparation and precise execution. Our process is designed to ensure the highest quality and durability for your foundation and wall repairs.

Understanding the Epoxy Injection System
An effective epoxy injection system relies on several key components working in harmony:
- Epoxy Resins: These are the heart of the system. We use high-strength, low-viscosity, and often moisture-tolerant resins. The low viscosity allows the epoxy to penetrate even the finest cracks (as narrow as 0.002 inches), ensuring a complete fill. For wider cracks or specific conditions, we might use gel-viscosity epoxies. These resins adhere to strict standards like ASTM C881, which specifies their properties for concrete bonding.
- Epoxy Paste (Cap Seal): This non-sagging paste is used to seal the surface of the crack and bond the injection ports in place. It prevents the injected liquid epoxy from simply flowing out of the crack during the injection process.
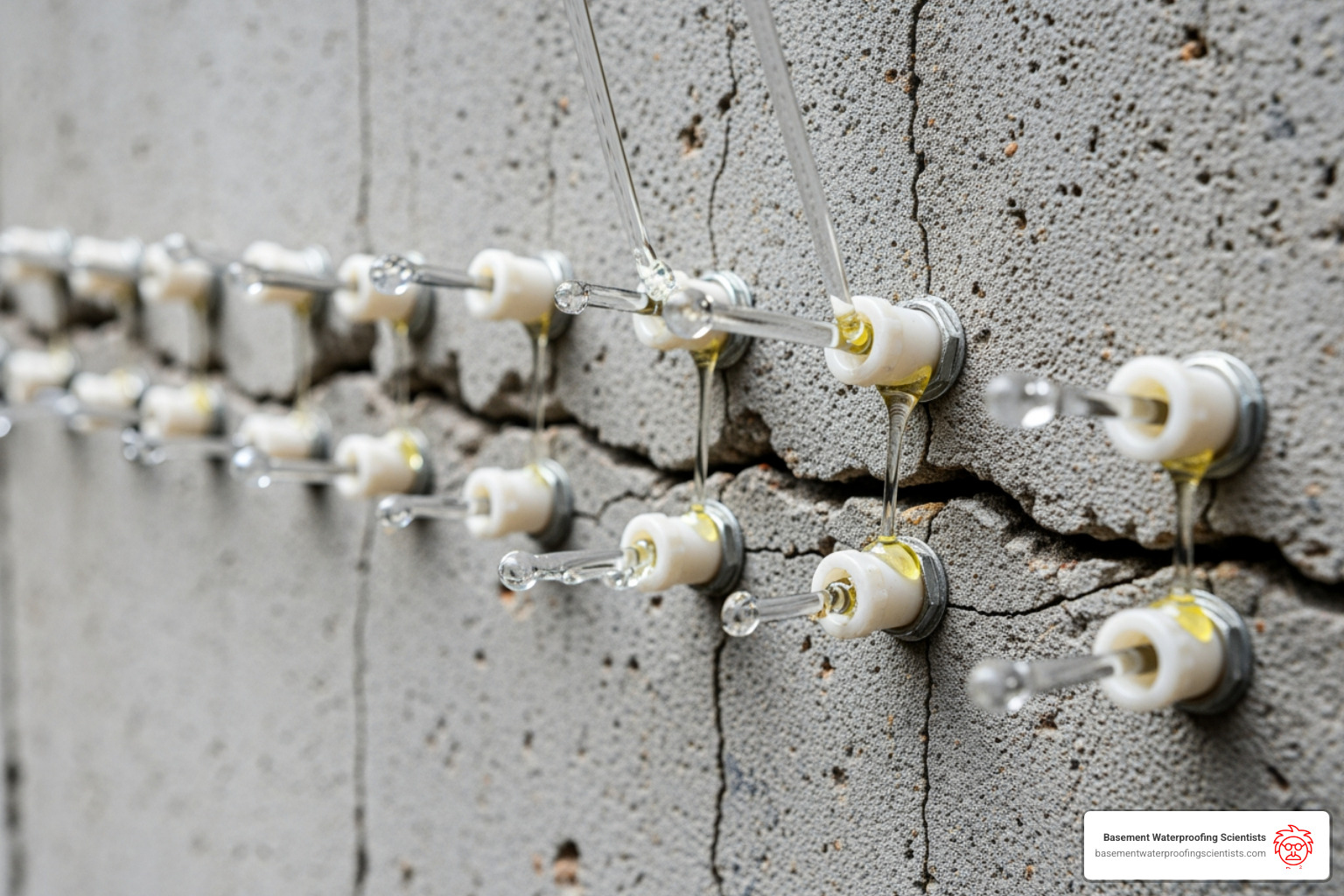
- Injection Ports: These small plastic fittings are strategically placed along the crack. They serve as entry points for the epoxy resin and allow us to monitor the flow and ensure the crack is fully saturated.
- Dispensing Equipment: Specialized pumping systems, including air guns or hand-actuated delivery systems, are used to inject the epoxy resin under controlled pressure. Typical injection pressures range from 50 to 100 psi, though very fine cracks might require over 200 psi for optimal penetration.
Preparing the Crack and Performing the Repair
Our step-by-step approach ensures a thorough and lasting repair:
- Crack Inspection and Measurement: First, we conduct a detailed inspection to understand the crack’s nature, cause, and width. We use crack gauge cards to accurately measure crack width, which helps us select the right epoxy resin and injection technique.
- Surface Cleaning: The crack area must be carefully clean for the epoxy to bond effectively. We clean the surface about 1/2 inch wide on each side of the crack, often using wire brushing, followed by compressed air or a vacuum to remove all dust, debris, and contaminants. If the concrete is deteriorated, we may V-groove the crack until sound concrete is reached.
- Port Installation and Sealing: We install surface-mounted injection ports along the crack, typically spaced 6-10 inches apart, depending on the crack’s depth and width. The epoxy paste (cap seal) is then applied over the crack and around the ports, creating a sealed channel. This paste is usually applied at about 1/8 inch thickness and 1 inch wide along the crack. We allow this paste to cure before injection.
- Injecting the Resin: Once the cap seal is cured, we begin the injection. For vertical cracks, we start at the lowest port and work our way up. For horizontal cracks, we start at the widest section. We inject the epoxy under pressure, continuously monitoring the adjacent port. When epoxy oozes from the next port, we know the section is filled, and we cap the completed port before moving to the next. This ensures the entire crack is filled from bottom to top.
- Curing Process: After injection, the epoxy needs time to cure. Most epoxies require a minimum of 12 hours to cure, though this can be longer in cooler temperatures (below 50°F). We ensure proper curing conditions are met for maximum strength development.
- Finishing: Once fully cured, we remove the injection ports and grind off any excess capping paste for a clean finish.
This meticulous process ensures that the structural integrity of your concrete is fully restored. You can learn more about this in our detailed guide on Concrete Wall Crack Repair Epoxy Injection.
Safety Precautions When Working with Epoxy
Working with epoxy materials requires strict adherence to safety protocols. Our team is trained to handle these materials safely, protecting both themselves and your property. Key safety precautions include:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): This includes wearing protective clothing, chemical-resistant gloves (rubber gloves), and safety eyewear to prevent skin and eye contact.
- Adequate Ventilation: Epoxies can release fumes, so proper ventilation is crucial, especially in enclosed spaces like basements.
- Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS): We always have MSDS available for all epoxy products used, which provides detailed information on hazards and safe handling procedures.
- Emergency Preparedness: Having eye wash facilities and appropriate cleaning materials readily available is essential in case of accidental exposure.
Our commitment to safety is paramount, ensuring that every epoxy injection job is performed with the utmost care. For more information on safely repairing foundation issues, refer to Basement Foundation Wall Repairing Crack Injection.
Epoxy Injection vs. Other Crack Repair Methods
Choosing the right crack repair method is crucial for a lasting solution. While epoxy injection is excellent for structural repairs, it’s important to understand how it compares to other common methods like polyurethane foam injection and crystalline waterproofing. Each has its strengths and ideal applications.
| Feature | Epoxy Injection | Polyurethane Foam Injection | Crystalline Waterproofing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Structural repair, moisture reduction | Waterproofing, sealing active leaks | Waterproofing, self-healing |
| Flexibility | Rigid, no flexibility | Flexible, accommodates crack movement | Becomes integral part of concrete, reacts to water |
| Structural Bond | Restores structural integrity, strong bond | No structural bond, only fills void | No structural bond, chemically waterproofs |
| Active Leaks | Not suitable (epoxy doesn’t react with water) | Excellent (expands upon contact with water) | Effective (reacts with water to form crystals) |
| Best Use Cases | Dormant structural cracks, dry/slightly damp | Active water leaks, moving cracks | General waterproofing, preventing future leaks |
| Material Type | Thermosetting polymer | Hydrophilic or hydrophobic foam | Cementitious material with active chemicals |
Polyurethane Foam Injection
When dealing with actively leaking cracks, polyurethane foam injection often takes center stage. Unlike epoxy, polyurethane is specifically designed for waterproofing and active water leaks. It’s a flexible material that reacts with water to expand, forming a watertight seal. This expansion allows it to effectively fill voids and seal cracks, even if they are wet or actively seeping water.
However, it’s crucial to remember that polyurethane foam primarily provides a waterproofing solution; it does not restore the structural integrity of the concrete. It’s a fantastic solution for keeping water out, particularly for those pesky Crack in Basement Wall Leaking Water issues, but it won’t re-bond the concrete back together.
Crystalline Waterproofing
Crystalline waterproofing represents another distinct approach. This method involves applying a cementitious coating containing specialized chemicals that react with the moisture and free lime in concrete. This reaction produces insoluble crystals that penetrate deep into the concrete’s capillaries and pores, effectively blocking water passage.
The beauty of crystalline waterproofing is its ability to become an integral part of the concrete, offering permanent waterproofing and even some self-healing properties as new hairline cracks can trigger further crystal growth. While it’s excellent for overall waterproofing and preventing water ingress, it doesn’t provide the same structural bonding and reinforcement that epoxy injection offers. It’s a powerful tool in our arsenal for comprehensive solutions like Waterproofing Basement Floor.
Verifying the Repair and Understanding Limitations
Once an epoxy injection is completed, verifying its effectiveness is a critical step in ensuring a successful and lasting repair. We employ various methods to confirm that the epoxy has fully penetrated the crack and restored the concrete’s structural integrity.
How We Verify the Effectiveness of an Epoxy Injection Repair
- Visual Inspection: Initially, we visually inspect the crack to ensure the epoxy has filled it completely and no voids or unsealed areas remain.
- Test Cores: For critical structural repairs, we may take test cores (typically 2 inches in diameter) from the repaired area. These cores are then examined to check for epoxy penetration depth and uniformity. They can also be tested for compressive and bond strength (per ASTM C 42) to confirm the repair’s structural performance.
- Non-Destructive Evaluation (NDE): Advanced NDE methods like Impact Echo (IE), Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV), and Spectral Analysis of Surface Waves (SASW) can be used to assess the integrity of the repaired crack without damaging the concrete. These techniques help us understand how well the epoxy has bonded and if the structural continuity has been restored.
These verification steps are essential to our quality assurance process, aligning with best practices outlined in technical guides such as A technical guide on structural crack repair.
When Epoxy Injection is NOT the Right Solution
While epoxy injection is a powerful tool, it’s not a universal fix. There are specific scenarios where it is not the appropriate solution:
- Active Leaks: Epoxy resins will not displace or react with water. If a crack is actively leaking, the water can create channels through the epoxy, rendering it largely ineffective for waterproofing. In such cases, polyurethane injection is usually a better choice.
- Moving or Dynamic Cracks: Epoxy is a rigid material. If a crack is subject to ongoing movement (e.g., due to thermal expansion/contraction, or continuous soil settlement), the cured epoxy will likely re-crack. For these situations, flexible materials like polyurethane are more suitable.
- Cracks Wider Than 1/4 Inch: While some epoxies can handle slightly wider cracks, those significantly exceeding 1/4 inch may be too large for effective and economical epoxy injection. Other repair methods might be more appropriate.
- Cracks from Ongoing Settlement: If the underlying cause of cracking is continuous structural settlement, injecting epoxy without addressing the root cause is a temporary fix at best. The crack will simply reappear. The underlying settlement issue must be resolved first.
- Corroding Rebar Issues: Cracks caused by corroding reinforcing steel should not be repaired by epoxy injection alone. The continuing corrosion will cause new cracks to appear adjacent to the repair, as the expanding rust will continue to stress the concrete.
Understanding these limitations is crucial to avoid Don’t Let These Foundation Repair Mistakes Damage Your Home.
Key Considerations for a Successful Epoxy Injection Repair
Achieving a successful epoxy injection repair requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Cause of the Crack: The most critical step is to accurately identify and, if possible, address the underlying cause of the crack. If the cause is ongoing, any repair will eventually fail. Our specialized equipment helps us pinpoint the root cause before recommending a solution.
- Moisture Conditions: Most structural epoxies perform best in dry or slightly damp conditions. The presence of significant moisture or active water flow can compromise the bond.
- Temperature During Application: Ambient and concrete temperatures significantly affect epoxy’s viscosity, pot life, and curing time. We adjust our materials and methods to suit the conditions in your Philadelphia, Reading, or Ardmore basement. Epoxies cure very slowly in temperatures below 50°F and can be difficult to work with.
- Selecting the Correct Resin Viscosity: Matching the epoxy’s viscosity to the crack width is paramount for optimal penetration. Low-viscosity epoxies are essential for hairline cracks (0.010 inches or smaller), while wider cracks might allow for medium or gel-viscosity products.
- Professional Assessment: This is where our 30 years of experience truly shine. A professional assessment by experts like us ensures that the crack is correctly diagnosed, the most appropriate repair method is chosen, and the application is performed to industry standards. We customize solutions for homes throughout Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware.
Conclusion
Epoxy injection is an invaluable method for restoring the structural integrity of cracked concrete foundations and walls. It offers high tensile and compressive strengths, often surpassing the original concrete, and provides excellent resistance to moisture penetration. When applied to the right type of crack—namely, dormant structural cracks in dry to slightly damp conditions—it delivers a durable, long-lasting repair that reinforces your home’s safety and longevity.
However, as we’ve explored, epoxy injection is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It’s crucial to understand its limitations, especially when dealing with active leaks, dynamic cracks, or cracks caused by ongoing structural issues. For these situations, alternative methods like polyurethane foam injection or crystalline waterproofing may be more suitable.
The key to any successful foundation repair lies in accurate diagnosis and expert application. With our 30 years of experience in basement waterproofing and structural repairs, we at Basement Waterproofing Scientists are equipped with specialized equipment to identify leak sources and provide customized solutions. We proudly serve homeowners across Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware, including Philadelphia, Reading, Norristown, Pottstown, and many other communities. Our commitment to quality is backed by a lifetime guarantee, giving you peace of mind.
Don’t let concrete cracks compromise your home’s foundation. If you’re concerned about cracks in your basement walls or foundation, let our experts provide a thorough assessment and recommend the most effective solution. Contact our experts for a comprehensive basement wall crack repair assessment today!